Introduction to PLC Panels
PLC panels are the central control hubs for automated industrial processes. They house the PLC, power supplies, input/output (I/O) modules, communication interfaces, and other necessary components to manage and control machinery and equipment. These panels are designed to be robust, reliable, and easily maintainable, ensuring the continuous and efficient operation of industrial systems.
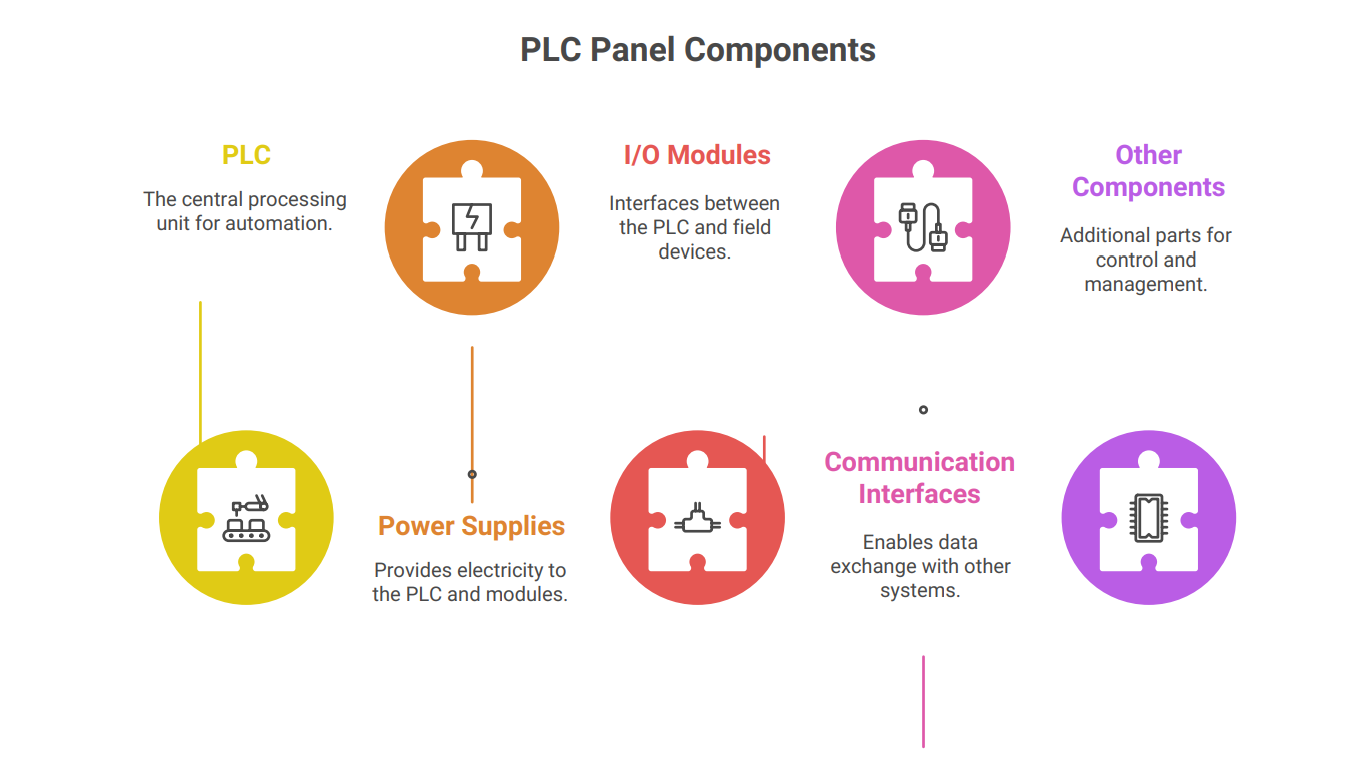
Key Components of a PLC Panel
A typical PLC panel consists of several essential components, each playing a crucial role in the overall functionality:
• Programmable Logic Controller (PLC): The brain of the system, responsible for executing the control logic programmed by the user. It receives input signals from sensors and field devices, processes them according to the program, and generates output signals to control actuators and other equipment.
• Power Supply: Provides the necessary voltage and current to power the PLC, I/O modules, and other components within the panel. Redundant power supplies are often used in critical applications to ensure continuous operation in case of a power supply failure.
• Input/Output (I/O) Modules: These modules interface the PLC with the outside world. Input modules receive signals from sensors, switches, and other input devices, converting them into a format that the PLC can understand. Output modules send signals from the PLC to actuators, motors, valves, and other output devices. Common I/O types include digital (discrete) and analog.
• Communication Modules: Enable the PLC to communicate with other devices, such as Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs), Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, and other PLCs. Common communication protocols include Ethernet/IP, Modbus, Profibus, and Profinet.
• Terminal Blocks: Provide a convenient and organized way to connect field wiring to the PLC and I/O modules. They simplify wiring and troubleshooting.
• Relays and Contactors: Used to switch high-power circuits, such as those controlling motors and heaters. They are controlled by the PLC's output signals.
• Circuit Breakers and Fuses: Protect the panel's components from overcurrent and short circuits.
• Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Although not always physically located within the PLC panel, the HMI is a critical component of the overall control system. It provides a user-friendly interface for operators to monitor and control the process.
• Enclosure: The enclosure houses all the components and protects them from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and temperature extremes. Enclosures are typically made of steel, stainless steel, or fiberglass.
Design Considerations for PLC Panels
Designing a PLC panel requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and safety:
• Environmental Conditions: The panel must be designed to withstand the environmental conditions in which it will be installed, including temperature, humidity, dust, and vibration.
• Power Requirements: The power supply must be sized appropriately to meet the power demands of all the components within the panel.
• Wiring and Cable Management: Proper wiring and cable management are essential for ensuring reliable operation and ease of maintenance. Wires should be neatly organized, labeled, and properly terminated.
• Safety: Safety is paramount in PLC panel design. The panel must be designed to meet all applicable safety standards and regulations. Safety features such as emergency stop buttons, safety relays, and interlocks should be incorporated.
• Accessibility: The panel should be designed to allow easy access to all components for maintenance and troubleshooting.
• Future Expansion: The panel should be designed with future expansion in mind. Sufficient space and spare I/O capacity should be provided to accommodate future additions or modifications.
• Documentation: Complete and accurate documentation is essential for the long-term maintenance and support of the PLC panel. Documentation should include wiring diagrams, component lists, and PLC program documentation.
Functionality of PLC Panels
PLC panels perform a wide range of functions in automated industrial processes, including:
• Process Control: Controlling the operation of machinery and equipment based on pre-programmed logic.
• Data Acquisition: Collecting data from sensors and field devices for monitoring and analysis.
• Alarm Management: Detecting and responding to abnormal conditions, such as equipment failures or process deviations.
• Sequence Control: Executing a sequence of operations in a specific order.
• Motion Control: Controlling the movement of motors and other actuators.
• Communication: Communicating with other devices, such as HMIs, SCADA systems, and other PLCs.
Applications of PLC Panels
PLC panels are used in a wide variety of industries and applications, including:
• Manufacturing: Controlling assembly lines, robotic systems, and other manufacturing equipment.
• Oil and Gas: Controlling pipelines, refineries, and offshore platforms.
• Water and Wastewater Treatment: Controlling pumps, valves, and other equipment in water and wastewater treatment plants.
• Power Generation: Controlling power plants and substations.
• Food and Beverage: Controlling food processing and packaging equipment.
• Pharmaceutical: Controlling pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
• Building Automation: Controlling HVAC systems, lighting, and security systems.
Maintenance of PLC Panels
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the reliable operation of PLC panels. Maintenance tasks include:
• Visual Inspection: Inspecting the panel for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
• Cleaning: Cleaning the panel to remove dust and debris.
• Testing: Testing the power supply, I/O modules, and other components to ensure they are functioning properly.
• Calibration: Calibrating sensors and other instruments.
• Software Updates: Updating the PLC software to the latest version.
• Backup: Regularly backing up the PLC program.
• Thermographic Scanning: Using infrared cameras to detect hot spots, which can indicate loose connections or failing components.
Conclusion
PLC panels are a critical component of modern industrial automation systems. By understanding their purpose, components, design considerations, functionality, applications, and maintenance requirements, engineers and technicians can ensure the reliable and efficient operation of these essential control hubs. Proper design, installation, and maintenance of PLC panels are crucial for maximizing productivity, minimizing downtime, and ensuring the safety of industrial processes.